43 label the carrier proteins in model 3
Solved Model 3 - The Electron Transport Chain Outer - Chegg 15. Label the carrier proteins in Model 3. 16. What substance do the carrier proteins transport across the innet mitochondrial membrane! Read This! NADH and ...1 answer · Top answer: 14. The site for Electron Transport Chain is the inner membrane of mitochondria. 15. 16. carrier proteins carry many factors in the ETC like electrons ... PDF Phospholipid & Membrane Transport Kit Student Handout 3 You will use a simplified representation of the phospholipid bilayer in this activity. 1. Label thehydrophilic headand hydrophobic tailin the photos below. CPK Color Scheme Oxygen (red) Nitrogen (blue) Hydrogen (white) Carbon (grey) Phosphorus (yellow) Center area is a convenient way to hold the phospholipids together to form membranes.
Proteomics of Skin Proteins in Psoriasis: From Discovery and ... Of the five proteins selected for verification, solution- based label-free analysis identified one peptide for ADP/ATP translocase 2 (Slc25a5), two peptides for Stefin A1, three peptides for KLK6 serine protease, and three peptides for Rab18 ( Table I ). Overall, the solution-based method identified 1544 proteins (6775 peptides).
Label the carrier proteins in model 3
PDF Student Handout 3 - 3D Molecular Designs You will use a simplified representation of the phospholipid bilayer in this activity. 1. Label thehydrophilic headand hydrophobic tailin the photos below. Color Scheme Oxygen (red) Nitrogen (blue) Hydrogen (white) Carbon (grey) Phosphorus (yellow) Center area is a convenient way to hold the phospholipids together to form membranes. 2. Peptide Modifications: KLH, BSA, OVA Conjugates - LifeTein OVA (ovalbumin) is a protein isolated from hen egg whites, that has a MW of 45 × 103 Da. It is often used as a second carrier protein to confirm that antibodies are specific for the peptide rather than the carrier protein (e.g. BSA). Thiol group modifications (via a Cys side chain) are used for KLH, BSA, or OVA conjugation. PDF 3 Protein Structure-S - Norwell High School With your group, write a grammatically correct sentence that summarizes how the secondary protein structure is formed from the primary structure. Protein Structure 5 Model 3 - Protein Structure (Part B) Tertiary Structure H CH 2 CH 3CH 3 CH
Label the carrier proteins in model 3. Solved Model 3 - The Electron Transport Chain H Η' Η' cell - Chegg Label the carrier proteins in Model 3. (Which ones are the cytochromes?) 16. What substance do the carrier proteins transport across the Question: Model 3 - The Electron Transport Chain H Η' Η' cell wall dectron oxygen cell membrane ADP ATP NADH NAD FADH FAD (HO) 14. What cell structure is the site for the electron transport chain? ATP.docx - ATP\u2014The Free Energy Carrier How does the ATP molecule ... ATP— The Free Energy Carrier 3. Model 3 - The ATP Cycle 9. Label the two large arrows in Model 3 with "hydrolysis" and ... Cellular processes (muscle contration, protein synthesis, cell division, etc.) b. Name at least two other cellular processes that could be fueled by the hydrolysis of ATP that are not listed in Model 3 or the ... 13 Cellular Respiration-S - North Kitsap School District Label the carrier proteins in Model 3. 16. What substance do the carrier proteins transport across the inner mitochondrial membrane? Read This! NADH and FADH 2 molecules release hydrogen ions that are transported across the inner mitochondrial membrane with the help of electrons. The result of these multiple processes is the production of large PDF Chapter 7: Membrane Structure and Function - BIOLOGY JUNCTION Membrane proteins are the mosaic part of the model. Describe each of the two main categories: integral proteins . peripheral proteins . ... 23. On the diagram below, add these labels: facilitated diffusion with a carrier protein, facilitated diffusion with a channel protein, active transport with a carrier protein, simple diffusion. For each ...
Recombinant Human Light TNFSF14 carrier-free - BioLegend Stock solutions can also be prepared at 50 - 100 µg/mL in appropriate sterile buffer, carrier protein such as 0.2 - 1% BSA or HSA can be added when preparing the stock solution. Aliquots can be stored between 2°C and 8°C for up to one week and stored at -20°C or colder for up to 3 months. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. Activity carrier protein Flashcards | Quizlet carrier protein. Proteins that change shape to allow a substance to pass through the plasma membrane. phagocytosis. the engulfing of food by a cell. facilitated diffusion. Facilitated Diffusiona passive form of carrier transport. exocytosis. the process by which wastes are packaged in vesicles and leave the cell. PDF Reading Guide - Leology 5. icwer 6. mcre again and cycle re peaks trans 23. di C On the diagram below, add these labels: facilitated diffusion with a carrier protein, facilitated diffusion with a channel protein, simple-diffusion. For each type of transport, give an example of a material that is moved in this manner. — achvc carrier (qtutc3e 24. H 2 O Model 3 The Electron Transport Chain Outer mitochondrial membrane ... Label the carrier proteins in Model 3. 16. What substance do the carrier proteins transport across the inner mitochondrialmembrane? HYDROGEN IONS (H+) HYDROGEN IONS ( H+ ) Read This! NADH and FADH2molecules release hydrogen ions that are transported acrossthe inner mitochondrial membrane with the help of electrons.
PDF Chapter 7: Membrane Structure and Function Membrane proteins are the mosaic part of the model. Describe each of the two main categories: ... - 3 - 10. Label the following structures: ... Concept 7.2 Membrane structure results in selective permeability 11. Distinguish between channel proteins and carrier proteins. 12. Are transport proteins specific? Cite an example that supports your ... Biology A: Unit 3 Flashcards - Quizlet Channel proteins move substances across the membrane at a much faster rate than carrier proteins. Carrier proteins can allow much larger substances to cross the membrane than channel proteins do. Which type of transport does not require energy but uses carrier proteins to help move substances across the cell membrane? Facilitated Diffusion - BIO 264 Anatomy & Physiology I The second type of facilitated diffusion utilizes carrier proteins in the membrane and is known as carrier-mediated transport. Unlike the channel proteins, carriers bind to a specific solute on one side of the membrane which causes the carrier to change shape, allowing solute access to the other side of the membrane (think of a revolving door). PDF Model 1 Glycolysis - psd202.org Label the carrier proteins in Model 3. 16. What substance do the carrier proteins transport across the inner mitochondrial membrane? HYDROGEN IONS (H+) Read This! NADH and FADH 2 molecules release hydrogen ions that are transported across the inner mitochondrial membrane with the help of electrons.
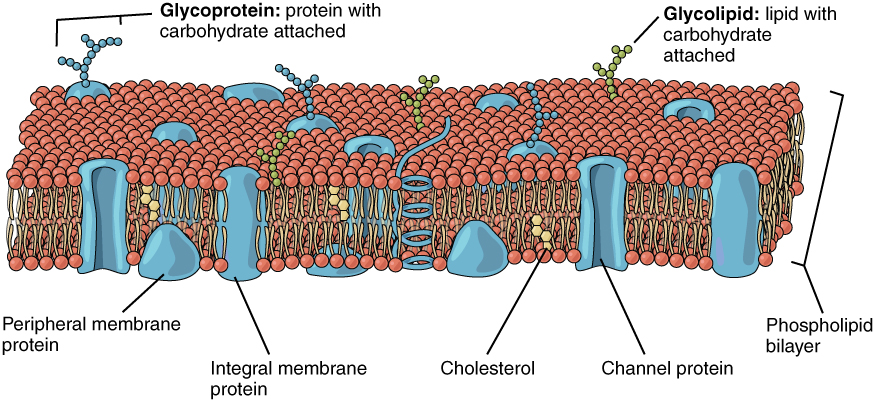
PDF Chapter 5: Cell Membranes and Signaling - Northern Highlands Regional ... Membrane proteins are the mosaic part of the model. Describe each of the two main categories: integral proteins peripheral ... - 3 - 10. Label the following structures: Glycolipid, glycoprotein, integral protein, peripheral protein, cholesterol ... carrier protein, simple diffusion. For each type of transport, give an example of a ...
PDF Chapter 3 Review Materials Key - wtps.org 9. What name is given to the transmembrane proteins that allow this direct passage? 3. Figure 3.3 is a simplified diagram of the plasma membrane. Structure A repre- sents channel proteins constructing a pore, structure B represents an ATP- energized solute pump, and structure C is a transport protein that does not depend on energy from ATP.
Cellular Respiration - 4J Blog Server 3. In the process of glycolysis, what happens to glucose after it crosses the cell membrane into the ... Label the carrier proteins in Model 3.5 pages
Carrier Proteins and Active Membrane Transport This schematic diagram shows carrier proteins functioning as uniporters, symporters, and antiporters. The tight coupling between the transport of two solutes allows these carriers to harvest the energy stored in the electrochemical gradientof one solute, typically an ion, to transport the other.
Integral Protein - Definition, Function, Structure, Quiz | Biology ... Many other proteins employ several alpha helices, which span the membrane. This allows for the creation of a protein channel, or a hole in the plasma membrane which allows various substances to pass.Common among bacteria is the third image, the beta barrel.. The Beta Barrel. A beta sheet is a complexly folded chain of amino acids which forms a flattened, rigid sheet.
GMP Recombinant Human IL-6 (carrier-free) - BioLegend Stock solutions can also be prepared at 50 - 100 µg/mL in appropriate sterile buffer, carrier protein such as 0.2 - 1% endotoxin-free BSA or HSA can be added when preparing the stock solution. Aliquots can be stored between 2°C and 8°C for up to one week or stored at -20°C or colder for up to 3 months. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. Activity
Efficient Preparation of Site-Specific Antibody-Drug Conjugates Using ... Post-translational modification catalyzed by phosphopantetheinyl transferases (PPTases) has previously been used to site-specifically label proteins with structurally diverse molecules. PPTase catalysis results in covalent modification of a serine residue in acyl/peptidyl carrier proteins and their …
Carrier Proteins: Definition, Function, and Examples A carrier protein is a type of protein in biology that transports a specific item across intracellular compartments, into the extracellular fluid, or between cells, as opposed to channel proteins, which are another form of membrane transport protein that transports molecules less selectively.




Post a Comment for "43 label the carrier proteins in model 3"